I have a Cisco 2801 router with IOS version 12.4(3e) and C2801-ADVIPSERVICESK9-M. I configured 2 site-to-site IPSec VPNs between the router & 2 other devices in France & Germany. Then, I configured an L2TP IPSec remote access VPN using pre-shared keys. I used Windows Vista to connect to the router and set up an L2TP IPSec remote access VPN. Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is another VPN protocol that is widely used in network World. At the beginning it has many vulnerabilities but after a while it is used with IPSec. IPSec provides extra security to L2TP. Here, the tunnel creation is done by L2TP and the encryptions is done by IPSec.
Contents
Introduction
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) over IPSec provides the capability to deploy and administer an L2TP VPN solution alongside the IPSec VPN and firewall services in a single platform. The primary benefit of the configuration of L2TP over IPSec in a remote access scenario is that remote users can access a VPN over a public IP network without a gateway or a dedicated line, which enables remote access from virtually any place with plain old telephone service (POTS). An additional benefit is that the only client requirement for VPN access is the use of Windows with Microsoft Dial-Up Networking (DUN). No additional client software, such as the Cisco VPN client software, is required.
This document provides a sample configuration for the native L2TP/IPSec Android client. It takes you through all the necessary commands required on a Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA), as well as the steps to be taken on the Android device itself.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the following software and hardware versions:
- Android L2TP/IPSec requires Cisco ASA software version 8.2.5 or later, version 8.3.2.12 or later, or version 8.4.1 or later.
- ASA supports Secure Hash Algorithm 2 (SHA2) certificate signature support for Microsoft Windows 7 and Android-native VPN clients when the L2TP/IPSec protocol is used.
- See Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI, 8.4 and 8.6: Configuring L2TP over IPSec: Licensing Requirements for L2TP over IPSec.
The information in this document was created from devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Configure
This section describes the information one would need in order to configure the features described in this document.
Configure the L2TP/IPSec Connection on the Android
This procedure describes how to configure the L2TP/IPSec connection on the Android:
- Open the menu, and choose Settings.
- Choose Wireless and Network or Wireless Controls. The available option depends on your version of Android.
- Choose VPN Settings.
- Choose Add VPN.
- Choose Add L2TP/IPsec PSK VPN.
- Choose VPN Name, and enter a descriptive name.
- Choose Set VPN Server, and enter a descriptive name.
- Choose Set IPSec pre-shared key.
- Uncheck Enable L2TP secret.
- [Optional] Set the IPSec identifier as the ASA tunnel group name. No setting means it will fall into DefaultRAGroup on the ASA.
- Open the menu, and choose Save.
Configure the L2TP/IPSec Connection on ASA
These are the required ASA Internet Key Exchange Version 1 (IKEv1) (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol [ISAKMP]) policy settings that allow native VPN clients, integrated with the operating system on an endpoint, to make a VPN connection to the ASA when L2TP over IPSec protocol is used:
- IKEv1 phase 1 - Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) encryption with SHA1 hash method
- IPSec phase 2 - 3DES or Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption with Message Digest 5 (MD5) or SHA hash method
- PPP Authentication - Password Authentication Protocol (PAP), Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol version 1 (MS-CHAPv1), or MS-CHAPv2 (preferred)
- Pre-shared key
Note: The ASA supports only the PPP authentications PAP and MS-CHAP (versions 1 and 2) on the local database. The Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) and CHAP are performed by proxy authentication servers. Therefore, if a remote user belongs to a tunnel group configured with the authentication eap-proxy or authentication chap commands and if the ASA is configured to use the local database, that user will be unable to connect.
Furthermore, Android does not support PAP and, because Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) does not support MS-CHAP, LDAP is not a viable authentication mechanism. The only workaround is to use RADIUS. See Cisco Bug ID CSCtw58945, 'L2TP over IPSec connections fail with ldap authorization and mschapv2,' for further details on issues with MS-CHAP and LDAP.
This procedure describes how to configure the L2TP/IPSec connection on the ASA:
- Define a local address pool or use a dhcp-server for the adaptive security appliance in order to allocate IP addresses to the clients for the group policy.
- Create an internal group-policy.
- Define the tunnel protocol to be l2tp-ipsec.
- Configure a domain name server (DNS) to be used by the clients.
- Create a new tunnel group or modify the attributes of the existing DefaultRAGroup. (A new tunnel group can be used if the IPSec identifier is set as group-name on the phone; see step 10 for the phone configuration.)
- Define the general attributes of the tunnel group that are used.
- Map the defined group policy to this tunnel group.
- Map the defined address pool to be used by this tunnel group.
- Modify the authentication-server group if you want to use something other than LOCAL.
- Define the pre-shared key under the IPSec attributes of the tunnel group to be used.
- Modify the PPP attributes of the tunnel group that are used so that only chap, ms-chap-v1 and ms-chap-v2 are used.
- Create a transform set with a specific encapsulating security payload (ESP) encryption type and authentication type.
- Instruct IPSec to use transport mode rather than tunnel mode.
- Define an ISAKMP/IKEv1 policy using 3DES encryption with SHA1 hash method.
- Create a dynamic crypto map, and map it to a crypto map.
- Apply the crypto map to an interface.
- Enable ISAKMP on that interface.
Configuration File Commands for ASA Compatibility
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) in order to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
This example shows the configuration file commands that ensure ASA compatibility with a native VPN client on any operating system.
ASA 8.2.5 or Later Configuration Example
ASA 8.3.2.12 or Later Configuration Example
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
This procedure describes how to set up the connection:
- Open the menu, and choose Settings.
- Select Wireless and Network or Wireless Controls. (The available option depends on your version of Android.)
- Select the VPN configuration from the list.
- Enter your username and password.
- Select Remember username.
- Select Connect.
This procedure describes how to disconnect:
- Open the menu, and choose Settings.
- Select Wireless and Network or Wireless Controls. (The available option depends on your version of Android.)
- Select the VPN configuration from the list.
- Select Disconnect.
Use these commands in order to confirm that your connection works properly.
- show run crypto isakmp - For ASA version 8.2.5
- show run crypto ikev1 - For ASA version 8.3.2.12 or later
- show vpn-sessiondb ra-ikev1-ipsec - For ASA version 8.3.2.12 or later
- show vpn-sessiondb remote - For ASA version 8.2.5
Note: The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) supports certain show commands. Use the Output Interpreter Tool in order to view an analysis of show command output.
Known Caveats
- Cisco bug ID CSCtq21535, 'ASA traceback when connecting with Android L2TP/IPsec client'
- Cisco bug ID CSCtj57256, 'L2TP/IPSec connection from Android doesn't establish to the ASA55xx'
- Cisco bug ID CSCtw58945, 'L2TP over IPSec connections fail with ldap authorization and mschapv2'
Related Information
Contents
Introduction
Layer 2 tunneling protocols, such as L2TP, do not provide encryption mechanisms for the traffic it tunnels. Instead, they rely on other security protocols, such as IPSec, to encrypt their data. Use this sample configuration to encrypt L2TP traffic using IPSec for users who dial in.
L2TP tunnel is established between the L2TP Access Concentrator (LAC) and the L2TP Network Server (LNS). An IPSec tunnel is also established between these devices and all L2TP tunnel traffic is encrypted using IPSec.
Prerequisites
Requirements

This document requires a basic understanding of IPSec protocol. To learn more about IPSec, please refer to An Introduction to IP Security (IPSec) Encryption.
IPSec Support Pages
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions.
Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.2(24a)
Cisco 2500 Series Routers
The information presented in this document was created from devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If you are working in a live network, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command before using it.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, see the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: To find additional information on the commands used in this document, use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) .
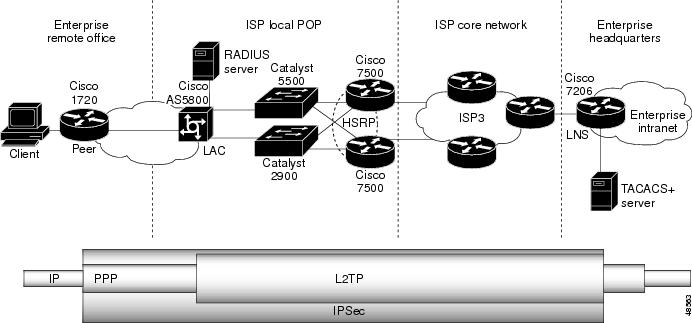
Network Diagram
This document uses the network setup shown in this diagram. The dial up user initiates a PPP session with the LAC over the analog telephone system. After the user is authenticated, the LAC initiates an L2TP tunnel to the LNS. The tunnel end points, LAC and LNS, authenticate each other before the tunnel is created. Once the tunnel is established, an L2TP session is created for the dialup user. To encrypt all the L2TP traffic between the LAC and LNS, the L2TP traffic is defined as the interesting traffic (traffic to be encrypted) for IPSec.
Configurations
This document uses these configurations.
| LAC Configuration |
|---|

| LNS Configuration |
|---|
Cisco L2tp Configuration
Verify
This section provides information you can use to confirm your configuration is working properly.
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
Use these show commands to verify the configuration.
show crypto isakmp sa— Displays all current IKE security associations (SAs) at a peer.
show crypto ipsec sa—Displays the settings used by current SAs.
show vpdn—Displays the information about the active L2TP tunnel.
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
Troubleshooting Commands
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Before issuing debug commands, please see Important Information on Debug Commands.
debug crypto engine—Displays engine events.
debug crypto ipsec—Displays IPSec events.
debug crypto isakmp—Displays messages about IKE events.
debug ppp authentication—Displays authentication protocol messages, including CHAP packet exchanges and Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) exchanges.
debug vpdn event—Displays messages about events that are part of normal tunnel establishment or shutdown.
debug vpdn error—Displays errors that prevent a tunnel from being established or errors that cause an established tunnel to be closed.
debug ppp negotiation—Displays PPP packets transmitted during PPP startup, where PPP options are negotiated.
Related Information

Comments are closed.