PHPMD - PHP Mess Detector This is the project site of PHPMD. It is a spin-off project of PHP Depend and aims to be a PHP equivalent of the well known Java tool PMD. PHPMD can be seen as an user friendly and easy to configure frontend for the raw metrics measured by PHP Depend. For all of the static configuration changes below involving the PHPStorm Preferences dialog, make sure you are clicking the 'Apply' button before clicking 'OK' to close the Preferences dialog. Note: native JSCS support is deprecated in PHPStorm 2020.2; it must be installed via a plugin. Go to PHPStorm preferences Other Settings JSCS. I had been using PhpStorm for years now and recommend it a lot for WordPress development. Simply put WordPress code base is significantly large and very convoluted. Good IDE is not just beneficial for it — it is indispensable. PhpStorm had steadily got more and more functionality, related to specific web development projects and standards. After years of hopes, whining to product manager on. The focus in setting up PHP Projects in PhpStorm, in particular a Laravel project. Composer with PHP with Easy Coding Standard (ECS), PHPUnit, and PhpStan. Also, some simplify projects to allow the output to be displayed in PHPStorm. Below are some other options, including psalm, Rector and PHP Mess Detector. Phpmd (PHP Mess Detector) is a static analysis tool that will find issues in your code you never knew you had. Your code will still run, follow a few of phpmd's recommendations though and it will be better!
Skip to end of metadataGo to start of metadataRedirection Notice
IconPhpStorm includes a great number of settings that may apply to the IDE, the editor or to the project we are working on. In this tutorial, we'll see where we can find these settings and how they are structured.
- IDE settings and Project settings
IDE settings and Project settings
PhpStorm can be configured on two levels: the IDE level and the project level. Project settings apply to the project we are working on. If we configure any of these options, they will only apply to the current project on the current machine. IDE settings are global for the IDE: they apply to every project opened, to the editor and so on.
Settings can be opened from the File | Settings menu, or by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S (CMD-, on Mac OS X). In the Settings dialog that opens, we can clearly see these two categories of settings in the list on the left: project settings first, then IDE settings.
Within the Settings dialog, we can easily search for specific settings. The search box at the top lets us search categories as well as individual settings. For example if we search for 'theme', the Appearance category will show up, highlighting a specific setting that lets us choose the theme used by PhpStorm.
IDE settings
IDE settings are stored in the user home directory. Check the web help for more information about the exact location. IDE settings can be shared with others by exporting/importing them from the File menu. See #Exporting and Importing IDE settings for more information.
Let's go over a few of the IDE settings. Again, these are global to the IDE on our machine and will be applied whenever we open a project in PhpStorm.
Under the Appearance category, we can pick the general IDE theme. I'm working with the Darcula theme here but there are different themes available.
IconMany more themes and color schemes are available at phpstorm-themes.com and ideacolorthemes.org.
One popular customization category is Colors & Fonts. Here we can find different color schemes which we can use in the editor. Subcategories show us a preview of these colors and allow us to customize them for different types of languages supported by the editor.
In other tutorials, we've already seen quite some keyboard shortcuts that can be used. From the Keymap category we can select different keymaps to resemble other software keyboard shortcuts. We can also assign shortcuts to menus and actions we often use. For example if we're using the Built-in REST Client in PhpStorm often, we can search for the action to open it and assign a keyboard shortcut to it.
Project settings
Project settings are stored in the .idea folder within the project. They can be shared with other developers on the team by simply sharing this folder, for example using VCS. Note that it's good practice not to share the workspace.xml file as this contains all the open editor tabs and such, which is nice to keep individualized.
Let's go over a few of the project settings categories. The first category is already an interesting one: coding styles. Depending on the project we are working on, we may want to have the IDE apply a different coding style. From the Code Style category, we can configure how we want code to be formatted.
IconBoth the WordPress and Drupal plugins for PhpStorm will automatically detect the framework used and propose changing the code style automatically.
Under the Inspections category, we can specify which inspections to enable or disable. Inspections will verify code and offer warnings, errors and often quick-fixes to improve code quality. It may make sense to enable them all but disabling some can also be useful.
IconPhpStorm also supports integrating PHP Code Sniffer and PHP Mess Detector as inspections.
Typically we can configure everything related to the project we are working on. Project settings may behave differently for some PhpStorm plugins. Some settings are in between IDE and project settings. For example Command Line Tools. We can run command line tools from within our IDE and we may want to have some default tools enabled across projects. The Command Line Tools category lets us choose where the tools are made available: either in the project or globally.
Default project settings
If you find out at some point that you're always configuring the exact same options for every project, you can make them into default project settings. The File | Default Settings menu lets us configure project settings which will be applied to every project created later on. For example, we can set the PHP interpreter options for all projects that are created in the future.
Exporting and Importing IDE settings
IDE settings are bound to our working environment, our current machine. What if we have multiple machines we want to work on? What if we want to share IDE settings with our team members? We can archive the IDE settings and distribute them using Dropbox, Google Drive or through source control.
From the File | Export Settings... menu, we can export our IDE settings. We can select all of them, or individual subcategories we want to export. For example, we may want to distribute Live Templates but not editor Colors and Fonts.
On other machines, we can use the File | Export Settings... menu to apply these settings in our IDE.
In addition to built-in coding assistance, PhpStorm provides checking the source code through integration with the PHP Mess Detector tool, which detects potential problems related to code size, inconsistency, unused code, violation of naming conventions, poor design, and so on.
To use PHP Mess Detector from PhpStorm instead of command line, you need to register it in PhpStorm and configure it as a PhpStorm code inspection. Once installed and enabled in PhpStorm, the tool is available in any opened PHP file, and no additional steps are required to launch it. The on-the-fly code check is activated upon every update in the file thus making it easy to get rid of discovered problems.
Errors and warnings reported by PHP Mess Detector on-the-fly are displayed as popup messages. When the tool is run in the batch mode, the errors and warnings are displayed in the Inspection Results tool window. Each message has the phpmd prefix to distinguish it from PhpStorm internal inspections.
You can have predefined rules applied or define your own custom set of rules.
Prerequisites
Prior to integrating PHP Mess Detector in PhpStorm, make sure the following prerequisites are met:
The directory containing the PHP engine executable must be added to the system
path. This allows code quality tool scripts execute calls to the system-wide PHP engine.For Docker Compose-based remote interpreters, make sure to use
execmode to avoid spawning additional containers.In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, go to PHP.
On the PHP page that opens, click next to the CLI Interpreter list.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog that opens, set the Lifecycle mode for the selected interpreter to Connect to existing container ('docker-compose exec').
Install and configure PHP Mess Detector
PHP Mess Detector scripts can be used as local scripts, the scripts associated with PHP interpreters, or scripts declared as project dependencies and installed via Composer, which is the preferable and recommended way.
Install PHP Mess Detector with Composer
Before you start, make sure Composer is installed on your machine and initialized in the current project as described in Composer dependency manager.
When you install PHP Mess Detector with Composer, PhpStorm automatically downloads the necessary scripts, registers them in the IDE, and, optionally, enables and configures the corresponding code inspection.
Inside composer.json, add the phpmd/phpmd dependency record to the
requireorrequire-devsection. Press Ctrl+Space to get code completion for the package name and version.Do one of the following:
Click the Install shortcut link on top of the editor panel.
If the Non-installed Composer packages inspection is enabled, PhpStorm will highlight the declared dependencies that are not currently installed. Press Alt+Enter and select whether you want to install a specific dependency or all dependencies at once.
Click next to the package record in the composer.json editor gutter to jump to the corresponding Settings/Preferences page and configure PHP Mess Detector manually.
Reset PHP Mess Detector configuration
After PHP Mess Detector is initially configured, further modifications in composer.json will not affect the inspection configuration. To apply newer changes, reset the PHP Mess Detector configuration.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, navigate to PHP | Quality Tools.
On the Quality Tools page that opens, expand the Mess Detector area and click next to the Configuration list.
In the PHP Mess Detector dialog that opens, empty the PHP Mess Detector path field.
Update the project Composer dependencies by clicking Update on top of the composer.json editor panel. See Update dependencies for details.
PhpStorm will perform the PHP Mess Detector configuration anew and thus apply the changes in composer.json.
Configure PHP Mess Detector manually
You can use the manually downloaded local PHP code quality tool scripts or scripts associated with PHP interpreters. There can be a number of local and remote PHP interpreters, the one specified on the PHP page of the Settings/Preferences dialog is considered Project Default. Learn more about configuring PHP interpreters in Configure remote PHP interpreters or in Configure local PHP interpreters.

Choose a PHP Mess Detector script to use
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, navigate to PHP | Quality Tools.
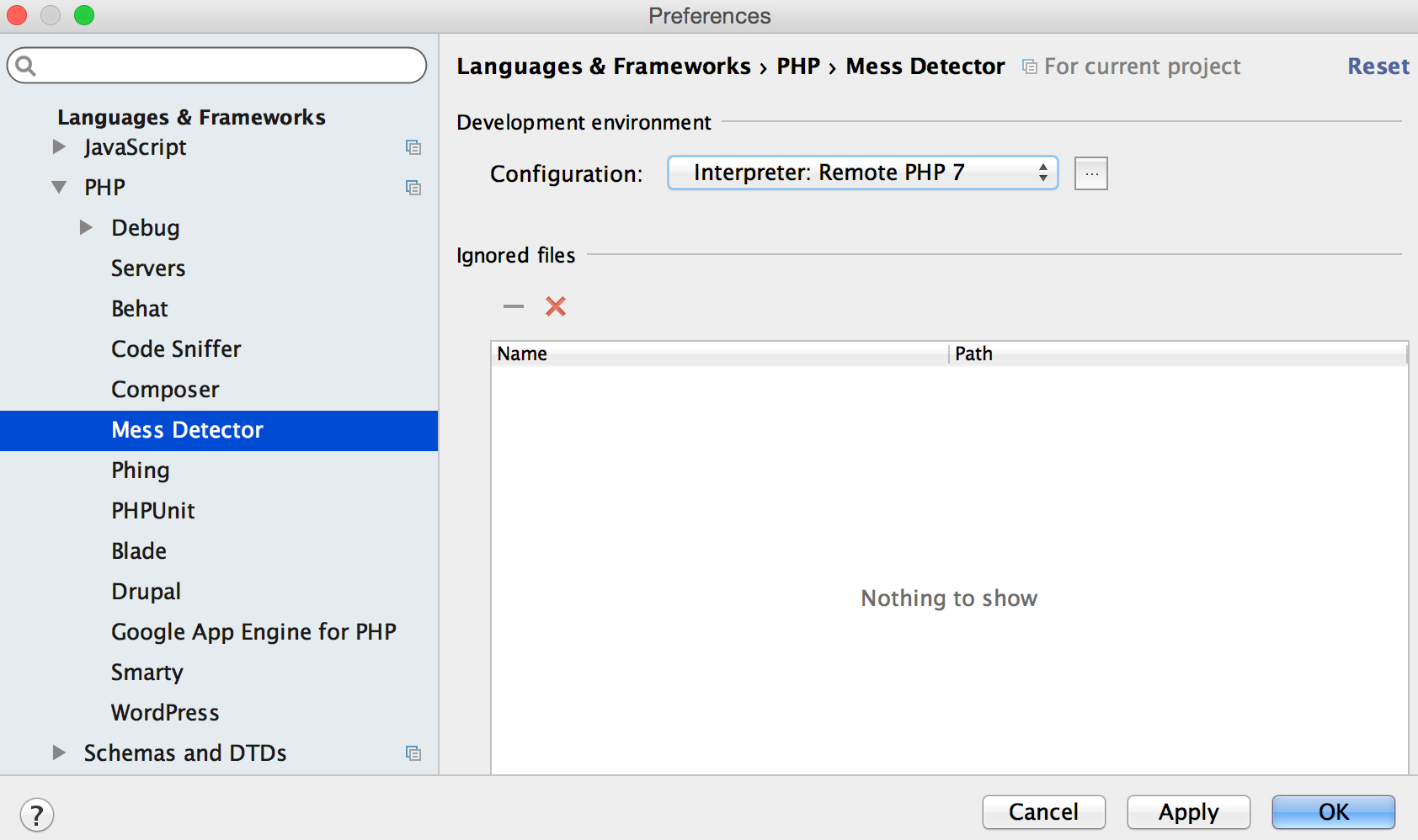
On the Quality Tools page that opens, expand the Mess Detector area. From the Configuration list, choose the PHP Mess Detector script:
To use the script associated with a specific remote PHP interpreter, choose the name of this interpreter.
To use a local script, choose Local. In this case the local PHP Mess Detector will be executed no matter which PHP interpreter - local or remote - is used in the project. Note that there can be only one Local configuration for PHP Mess Detector because PhpStorm runs a script (phpmd.bat for Windows or phpmd for Linux and macOS) that contains a path to a PHP engine.
To use the script associated with the default project interpreter, that is, the one chosen on the PHP page of the Settings/Preferences dialog, choose By default project interpreter.
Configure a local PHP Mess Detector script
Download and install the PHP Mess Detector scripts.
To check the PHP Mess Detector installation, switch to the installation directory and run the following command:
If the tool is available, you will get a message in the following format:
PHPMD version <version>To have code checked against your own custom coding standard, create it. Store the rules and the ruleset.xml file that points to them in the rulesets root directory.
Register the local PHP Mess Detector script in PhpStorm:
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, navigate to PHP | Quality Tools.
On the Quality Tools page that opens, expand the Mess Detector area and click next to the Configuration list.
In the PHP Mess Detector dialog that opens, specify the location of the phpmd.bat or phpmd PHP Mess Detector executable in the PHP Mess Detector path field. Type the path manually or click and select the relevant folder in the dialog that opens.
To check that the specified path to phpmd.bat or phpmd ensures interaction between PhpStorm and PHP Mess Detector, that is, the tool can be launched from PhpStorm and PhpStorm will receive problem reports from it, click the Validate button. This validation is equal to running the
phpmd --versioncommand. If validation passes successfully, PhpStorm displays the information on the detected PHP Mess Detector version.
If necessary, in the Tool process timeout field, specify how long you want PhpStorm to wait for a result from PHP Mess Detector, whereupon the process is terminated to prevent excessive CPU and memory usage.
Configure a PHP Mess Detector script associated with a PHP interpreter
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, navigate to PHP | Quality Tools.
On the Quality Tools page that opens, expand the Mess Detector area and click next to the Configuration list. The PHP Mess Detector dialog opens showing the list of all the configured PHP Mess Detector scripts in the left-hand pane, one of them is of the type Local and others are named after the PHP interpreters with which the scripts are associated.
Click on the toolbar. In the PHP Mess Detector by Remote Interpreter dialog that opens, choose the remote PHP interpreter to use the associated script from. If the list does not contain a relevant interpreter, click and configure a remote interpreter in the CLI Interpreters dialog as described in Configure remote PHP interpreters.
When you click OK, PhpStorm brings you back to the PHP Mess Detector dialog where the new PHP Mess Detector configuration is added to the list and the right-hand pane shows the chosen remote PHP interpreter, the path to the PHP Mess Detector associated with it, and the advanced PHP Mess Detector options.
If necessary, in the Tool process timeout field, specify how long you want PhpStorm to wait for a result from PHP Mess Detector, whereupon the process is terminated to prevent excessive CPU and memory usage.
Configure PHP Mess Detector as a PhpStorm inspection
Configure the PHP Mess Detector inspection with Composer
You can include the information on the default and custom PHP Mess Detector rulesets inside the scripts section of composer.json. When you install or update project dependencies, the specified rulesets will be detected and the PHP Mess Detector validation inspection will be enabled automatically.
If no ruleset is specified in the scripts section of composer.json, PhpStorm will additionally check the project root to locate the ruleset with the phpmd.xml default name. If the file is present, it will be automatically selected as the inspection's Custom ruleset.
In the
scriptssection of composer.json, add thephpmdPHP Mess Detector launch command into one of the leaf elements.Provide the names of the built-in standards or the paths to custom rulesets as the arguments to denote the coding standards used.
For example, adding the following record will select the Codesize and Controversial built-in rulesets, as well as the custom ruleset defined in the /my/src/custom_ruleset.xml file:
'scripts': { 'phpmd': 'phpmd codesize,controversial,/my/src/custom_ruleset.xml' }
After PHP Mess Detector is initially configured, further modifications in composer.json will not affect the inspection configuration. To apply newer changes, reset the PHP Mess Detector configuration on the PHP | Quality Tools page of the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S and update project dependencies.
Configure the PHP Mess Detector inspection manually
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, click Inspections under Editor.
On the Inspections page that opens, expand the PHP | Quality Tools node and select the checkbox next to PHP Mess Detector validation.
If you have installed PHP Mess Detector with Composer but the corresponding inspection is currently disabled, PhpStorm highlights its record in composer.json. Press Alt+Enter and use the provided Enable inspection quick-fix to enable the inspection and open the Inspections page.
In the right-hand pane, configure the PHP Mess Detector tool by using the controls in the Options area:
From the Severity list, choose the severity degree for the PHP Mess Detector inspection. The selected value determines how serious the detected discrepancies will be treated by PhpStorm and presented in the inspection results.
From the Scope list, choose the scope to limit the inspection application to.
Appoint the rules to apply.
To use predefined rules, in the Options area, select the checkboxes next to the validations to be performed.
To use a custom ruleset:
Create and save one or several ruleset files. A valid ruleset file is an .xml file that contains the
<ruleset>root element with thenameattribute. For more details on custom rulesets, see http://phpmd.org/documentation/creating-a-ruleset.html.In the Custom rulesets area, click and select the relevant rule definition file in the dialog that opens. When you click OK, a new item is added to the Custom rulesets list, where the Name field shows the ruleset name retrieved from the attribute
namewithin the<ruleset>tag and the File field shows the location of the selected ruleset file.
Phpstorm Cannot Run Php Mess Detector
Share a custom coding style with the team
Put the root directory of your coding standard under the project root.
Configure PHP Mess Detector as a PhpStorm inspection.
Appoint your coding standard.
Make sure that a project profile is selected at the top of the Inspections page. Such profiles are saved in a particular project's .idea directory (for example, $PROJECT_DIR$/.idea/inspectionProfiles ). See Configure profiles for details.
On the Version Control page of the Settings/Preferences dialog, make sure that the .idea directory is put under version control.
Phpstorm Mess Detectors
Run PHP Mess Detector in the batch mode
From the main menu, select Code | Inspect code.
Select the inspection profile from the list, or click to configure a new profile in the Inspections dialog that opens. You can also click to check, which fixes will be applied and make sure that the PHP Mess Detector validation inspection is enabled.
View the inspection results in the Inspection results tool window. Errors and warnings reported by PHP Mess Detector are prefixed with
phpmdto distinguish them from PhpStorm internal inspections.
Exclude files from PHP Mess Detector Validation inspection
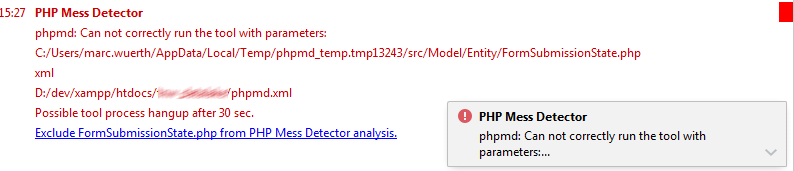
When waiting for Mess Detector response exceeds the limit specified in the Tool process timeout field in the Mess Detector dialog, PhpStorm suggests adding the file to the ignore list.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, navigate to PHP | Quality Tools.
On the Quality Tools page that opens, expand the Mess Detector area and click the Show ignored files link.
To add a file, click and locate the desired file in the dialog that opens.
To delete a file from the list and have Mess Detector process it again, select the file and click .
To remove all the files from the list, click .

Comments are closed.